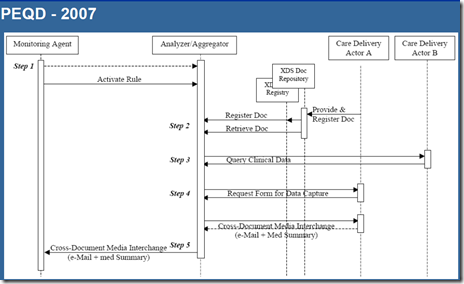
Steps 3, 4 & 5 – System costs and implementation
3. Understanding costs and financing options
· Planning
· Identify a member(s) of the project team to research the costs and potential subsidies or reimbursement programs available, including health-care provider incentives
· Identify any existing national and state initiatives for which the practice may qualify
· Calculate your practice’s projected reimbursement under the new Medicare incentive legislation and research pay-for-performance programs
· Technology
· Document price differences between a stand-alone and EHR system and include associated costs
4. Selecting a system
· Planning
· Involve the entire project team in system selection by defining specific evaluation criteria for comparison and facilitate open discussions about the pros and cons of each product and the rationale
· Develop your own test scripts or scenarios reflecting your practice’s common workflows, and ask each vendor to demonstrate how their product would work in those scenarios
· Contact other practices in your area that currently use the products you are evaluating
· Evaluate usability features of each software vendor
· Make sure you clearly understand what training is offered by the vendor and the costs
· Technology
· Ensure that the hardware required by the system supports your practice’s desired workflow, including efficiency, security, and hardware synchronization
· Select Internet connectivity with a redundant Internet connection backup in place
5. Deployment
· Planning
· Commit staff time during implementation for training and workflow integration
· Ensure that all affected members of the practice receive appropriate training
· Create an incremental approach to training over several days and schedule a few additional training sessions over the next few months
· Ask your vendor if they provide access to learning materials
· Technology
· The project leader should keep your software vendor informed about any technical problems or usability issues
· Log support cases with the technology provider
· Set default routing to electronically send prescriptions to the pharmacy rather than faxing them because the feature will be under used
· Utilize electronic prescription renewal functionality as this increases efficiency and improves patient service when they are able to get their prescriptions renewed more quickly
· Integrate patient demographic information from the practice management system in advance of e-prescribing implementation
· Designate a prescriber or staff person to retrieve and manage responses for renewal authorization requests that are sent electronically from pharmacies
· Make sure you know how to select your patient’s pharmacy of choice using your e-prescribing application
· Respond to electronic renewal requests as soon as possible, and always within 24 hours on business days to avoid duplicate renewal authorization requests
· Avoid queuing or “batching” prescriptions before sending them to pharmacies electronically to provide pharmacies adequate time to receive and fill the prescription
· Follow DEA regulations by refraining from electronic transmission of prescriptions for controlled substances until these regulations are changed to allow electronic transmission
· Communications
· Inform local pharmacies that you are getting ready to exchange prescription information electronically
· Communicate with patients about electronic prescribing and its benefits and remind them to call the pharmacy rather than the practice when they need their prescriptions renewed